Updated February 19, 2025
Mechanical aptitude tests are designed to assess your understanding and ability to apply basic mechanical and physical principles.
These tests measure your understanding of how mechanical systems work, including concepts such as force, motion, energy, and tools.
Join over 1,500 candidates who have enhanced their mechanical aptitude skills using our proven strategies.
What's on this page:
Here you'll find 35 Mechanical practice questions (Timed and Untimed) split into Mechanical and Electrical topics, to help you understand the real exam.
Tap on any of the topics below for instant access to helpful sample questions!
To get a better sense of what our practice tests look like, take this free Electricity interactive assessment.
To get a better sense of what our mechanical ability practice tests look like, take this free interactive assessment.
- Electricity: Questions in this category will evaluate your basic understanding of electrical concepts.
- Maintenance: Includes Applied mechanics questions such as PLC, Hydraulics, and Pneumatics.
- Simple Machines: Questions about simple machines test your understanding of basic mechanical devices like levers, pulleys, gears, and inclined planes.
- Kinematics (Velocity): Kinematics questions focus on motion geometry.
- Quantitative: Quantitative questions include mechanical questions that involve numerical calculations.
- Thermodynamics: Test your understanding of the influences of forces and torques (rotational forces) that are exerted on various objects.
- Force and Moment: This type of question tests your understanding of how forces affect the motion of objects.
This free mechanical aptitude test will cover questions from the more common Mechanical Aptitude tests, including questions with varying difficulty, format, content, and time frame.
Free Mechanical Aptitude Test with Answers
Mechanical aptitude tests (also known as mechanical reasoning tests) assess your basic mechanical knowledge, i.e., your ability to understand basic mechanical concepts and apply them to various scenarios.
The mechanical aptitude assessment test questions will usually contain one or more images followed by multiple-choice questions with a time limit, covering topics such as gears, thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and more. Let’s review a few examples, solving tips, and common exams that require mechanical knowledge.
Electricity
The mechanical electricity section within the mechanical aptitude exam focuses on understanding the components and principles of electrical circuits, including devices that store, resist, or control electrical energy.
Questions often involve identifying and understanding the function of electrical components like resistors, capacitors, diodes, and inductors, as well as applying concepts such as Ohm’s Law to solve for voltage, current, and resistance in various circuit configurations.
1. A device used to store electrical energy is called a:
A. Resistor.
B. Diode.
C. Capacitator.
D. Inductor
Answer:
The correct answer is C.
The question asks for the device that is used to store electrical energy. Let's go through the options one by one.
A. A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.
It is primarily used to limit current and/or divide voltages in electrical circuits. It doesn't store energy but rather dissipates it in the form of heat.
B. A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction but not another. It is commonly used for rectification (converting alternating current to direct current), among other applications.While it can be part of circuits that store energy, the diode does not.
C. A capacitor is an electrical component that stores and releases electrical energy in a circuit. It stores energy by accumulating an internal imbalance of electric charge between its plates, and it can release that stored energy when needed. Therefore, it is the device used to store electrical energy.
D. An inductor is an electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when an electrical current is passed through it. While it does store energy, it is not electrical energy per se but rather magnetic energy.
Moreover, it's commonly used to store energy temporarily and is often used in filtering applications and energy storage in inductive-based converters, but is not primarily designed for electrical energy storage in the way a capacitor is.
Based on the above explanations, the correct answer is C - Capacitor. This is the device that is specifically designed to store electrical energy in an electric field between its plates.
Looking for a different Mechanical Aptitude practice test? Check out the following pages for more specific practice:
Mechanical: Free IBEW Practice | Free Bennet Mechanical Practice | Free EIAT Practice | Free Ramsay Practice | Free CAST Practice | USPS 955 | Walmart Maintenance Test | EEI Test | NOCTI Test | ASVAB Mechanical Test
General Aptitude: Free Aptitude Practice | Free Cognitive Ability Practice | Free Personality Practice | Pre-Recorded Interview Guide & Tips | AI Interview
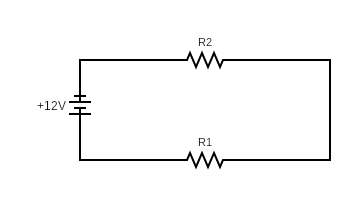
2. What is the total resistance if R1 = 4Ω and R2 = 6Ω?
A. 2Ω
B. 10Ω
C. 24Ω
D. 8Ω
Answer:
The correct answer is B.
In a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances:
Rtotal =R1+R2=4Ω+6Ω=10Ω.
Looking for the USPS Mechanical Preparation?
Prepare for the USPS 955 Maintenance test with our expert-curated PrepPack. Featuring hundreds of practice questions, thorough explanations, and professional tips, it’s your key to acing the test. Start your journey to a USPS career today!
So worth it
"Everything that I needed to know was in the study guide. I felt very prepared for the test and confident in my answers. I loved that they explained every possible answer and why some were better choices than others. Ordering this study guide was the best decision, it was so worth it".
Stephanie V. On USPS Exam 955 Practice
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (More reviews)
Electricity questions can also be found in our IBEW PrepPack, Ramsay Mechanical PrepPack, Ramsay Electrical PrepPack, NOCTI Electronics Technician, and CAST PrepPack. Let's look at two examples of specific questions from maintenance mechanical exams:
You can find more mechanical IQ test sample questions on our Free ASVAB Practice Test.
Pneumatics and Hydraulics
Pneumatics and hydraulics questions focus on the use of compressed air (pneumatics) and pressurized liquids (hydraulics) to perform mechanical work.
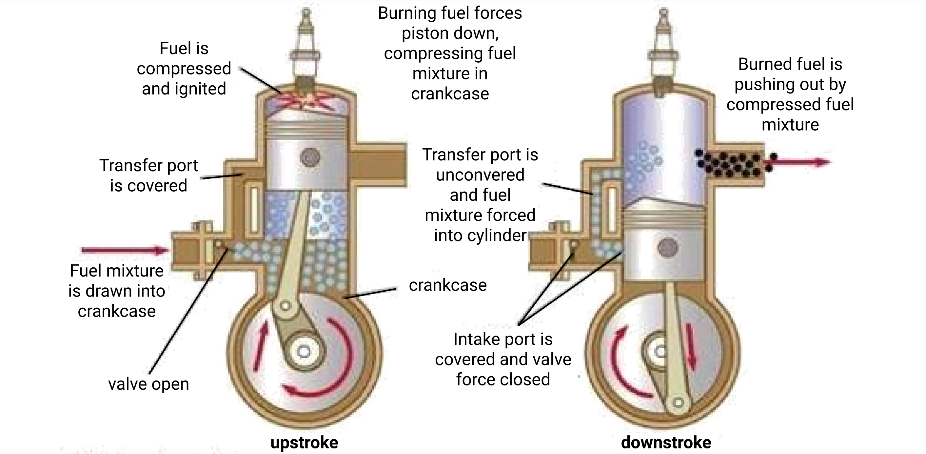
3. There are four cycles in IC Engines: compression, exhaust, intake, and expansion. In two-stroke engines, two functions are performed in one stroke.
Which of the following stages occurs simultaneously?
A. Compression and exhaust.
B. Intake and expansion.
C. Compression and intake.
D. None of the above.
Answer:
The correct answer is C. There are two processes involved in a two-stroke engine: Compression stroke and Power stroke.
In compression stroke, the inlet port opens and the air-fuel mixture enters the chamber, and the piston moves upwards, compressing the mixture.
In the power stroke, the heated gas exerts pressure, and the piston moves downwards during the expansion. Therefore, only C is the correct choice. The following figure summarizes the two-stroke engine cycles.
PLC and I/O
PLC and I/O questions focus on the components of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) used in industrial automation.
4. Which of the following executes logical commands to control sensors and actuators?
A. Processor.
B. I/O module.
C. RAM.
D. ROM.
Answer:
The correct answer is B.
The processor (CPU) reads the stored program in Random Access Memory (ROM) with the help of the operating system that is downloaded in Read-Only Memory (ROM).
The processor makes logical decisions based on the PLC program. However, these decisions are executed with the help of the I/O module. Therefore, B is the correct choice, and A, C, and D are incorrect.
Looking for the Amazon Maintainance Mechniacal Preparation?
JobTestPrep offers you a comprehensive Amazon Maintenance worker prep that includes:
- Three distinct practice tests tailored to the real Amazon test
- Full work simulation and behavioral assessment
- In-depth practice on topics like Tools, Hydraulics, and Electricity
Prepare for your Amazon test confidently with extensive practice for only $79.
Amazon Maintenance Technician Test Prep
"I am extremely satisfied! The customer service is amazing!".
Maria M. On Amazon Maintenance Technician Prep
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
Maintenance Mechanical Abilities questions can also be found in our USPS 955 PrepPack, Ramsay Maintenance PrepPack, Walmart Maintenance PrepPack, UPS Mechanic PrepPack, and Elevator (EIAT) Apprenticeship PrepPack, for people who want to become elevator mechanics. Let’s continue to different concepts in basic mechanics – beginning with Kinematics (Velocity).
Kinematics
Kinematics mechanic assessment test questions explore the motion of objects, focusing on how they move under the influence of various forces.
These questions often involve analyzing velocity, acceleration, displacement, and the relationships between different parts of a system in motion.
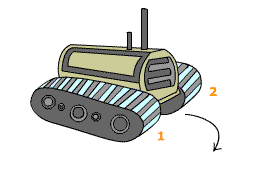
5. Which of the tractor chains will move more slowly if the tractor were to turn in the direction indicated by the arrow? If both chains are likely to move at the same speed, then select answer option 3.
Please select the correct answer.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
Answer:
The movement of the tractor can be paralleled to a circular motion problem in which the one travelling along the outer edge of the turn has a greater distance to cover.
Such is the case of chain 2. In contrast, chain 1 stays almost completely still, as it is the axis of the turn.
Therefore, chain 1 has to move slower in order for the tractor to move in the marked direction. The correct answer is A = 1.
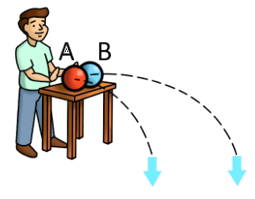
6. Which ball will reach the floor first? (If equal, Mark C.)
A. a
B. b
C. c
Answer:
The correct answer is C.
Gravity is applied to both balls equally, and the vertical distance they ought to pass is identical. The time needed for both balls to hit the ground is identical, regardless of the horizontal velocity component.
Therefore, it can be deduced that both balls will hit the ground simultaneously.
Remember the physical principle: When an object falls under the influence of gravity, its vertical velocity does not depend on the horizontal velocity.
Master Mechanical Problems with Solid Fundamentals
Learning physical principles is the key to solving mechanical problems and acing the mechanical test with confidence.
Memorizing specific answers isn't enough. Instead, understanding the fundamentals prepares you to tackle any question, no matter how it’s worded.
For just $79, you can gain access to our Mechanical Study Guide, where you’ll practice hundreds of real-world questions and reinforce your knowledge of core physical principles.
Mechanical Aptitude Test Practice
"Very Satisfied. I have been working with Controls, Logic, PLC's, VFD's, and automated equipment for 29 years and the information in these modules is the most accurate I have ever seen. #RECOMMEND".
James. On Mechanical Aptitude Test Practice
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
7. Which bird will experience less resistance flying? (If equal, mark C.)

A. a
B. b
C. c
Answer:
The correct answer is A.
In picture A, the bird flies with her wings backward, minimizing the contact surface with the wind and creating less resistance.
The bird in picture B extends with her wings and legs perpendicular to the wind direction, thus increasing the contact surface with the wind, creating much more resistance.
The same phenomenon makes a crumpled piece of paper fall faster than an open sheet of paper, which has more surface area and more resistance.
Remember the physical principle: The larger the surface of contact with air/wind, the more resistance (force) is created.
Kinematics questions may ask about basic concepts, and movements, and sometimes may include different types of calculations. Kinematics questions can also be found in our Ramsay Mechanical PrepPack, Bennett PrepPack, Wiesen PrepPack, and Delta BMAR PrepPack.
Another type of question that involves calculation is Quantitative questions. These questions may feel as if they should be included in Numerical Aptitude tests (and really are occasionally) – but they have great importance in mechanics. Let’s look at an example:
Quantitative Sample Question
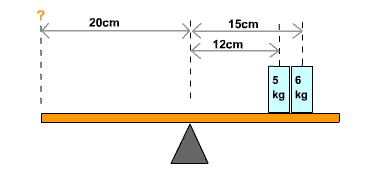
8. Two weights are placed on the right side of a lever, as shown in the picture below. What mass would you place 20 cm to the left of the fulcrum, in order to balance the lever?
A. 6.5 kg
B. 7 kg
C. 7.5 kg
D. 8 kg
Answer:
For the scale to balance, the total of torques on either side of the scale must be equal. Assigning the numbers 1, 2, and 3 to the weights of 5kg, 6kg, and the "?" weight, respectively, we have our torque equation: T1 + T2 = T3.
Each torque is by definition T = W x L, where W is the weight and L is the distance from the fulcrum. Recall that W = M x g, where M is the mass and g is the gravitational constant.
M1 x g x L1 + M2 x g x L2 = M3 x g x L3
We can simplify by dividing both sides by g:
M1 x L1 + M2 x L2 = M3 x L3
Our givens are M1 = 5kg, L1 = 12cm, M2 = 6kg, L2 = 15cm, M3 = ?, L3 = 20cm. Substituting the values given in the question in the equation:
5kg x 12cm + 6kg x 15cm = M3 x 20cm
Now solve like a regular equation (multiplying before adding and isolating M3), just do not forget to mind the units as well:
(5 x 12) [kg x cm] + (6 x 15) [kg x cm] = M3 x 20cm
Multiply the figures on the left side:
60 [kg x cm] + 90 [kg x cm] = M3 x 20cm
Add the figures on the left side:
150 [kg x cm] = M3 x 20cm
Divide by 20cm to isolate M3:
M3 = 150 [ kg x cm] / 20cm
M3 = (150/20) [kg x cm / cm]
=> M3 = 7.5kg
Therefore, 7.5 kg is the correct answer.
Looking for Ramsay Mechanical Test Preparation?
Achieve success on the Ramsay Mechanical Test with our comprehensive PrepPack, designed for all versions of the test, including those for Maintenance Technicians, Electricians, Auto Mechanics, and more.
What you get:
- Full Ramsay Mock Simulations to mirror the real test.
- Focused practice tests for different mechanical question types.
- Detailed explanations and tips to improve your skills.
- Extensive study guides to ensure your success.
Start practicing today for just $79—your future starts now!
Ramsey test for Goodyear
"I purchased this test prep and studied for four days and passed the Ramsey test for Goodyear, I'm sure if I had more time I would have done even better. Thank you".
Terry H. On Ramsay Mechanical Test
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (More reviews)
Let’s continue to the next question type – Dynamics – and mainly Thermodynamics.
Thermodynamics
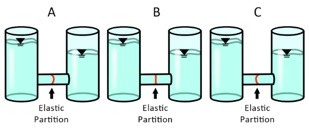
9. Which of the three following diagrams is correct?
A. a
B. b
C. c
Answer:
A pressure difference on both sides causes the bending of the partition. That pressure difference is determined by the level of water in each container.
The pressure is determined by the height of the water on the container – the higher the water – the greater the pressure.
In A, the partition bends to the right, suggesting the pressure is greater on the left side. That is consistent with the higher water level on the left side.
In B, the partition is flat, suggesting there is no pressure difference between its two sides despite the different water levels. Therefore, this answer is false.
In C, the partition bends to the left, suggesting the pressure is greater on the right side. That contradicts the higher water level on the left side. Therefore, this answer is also false.
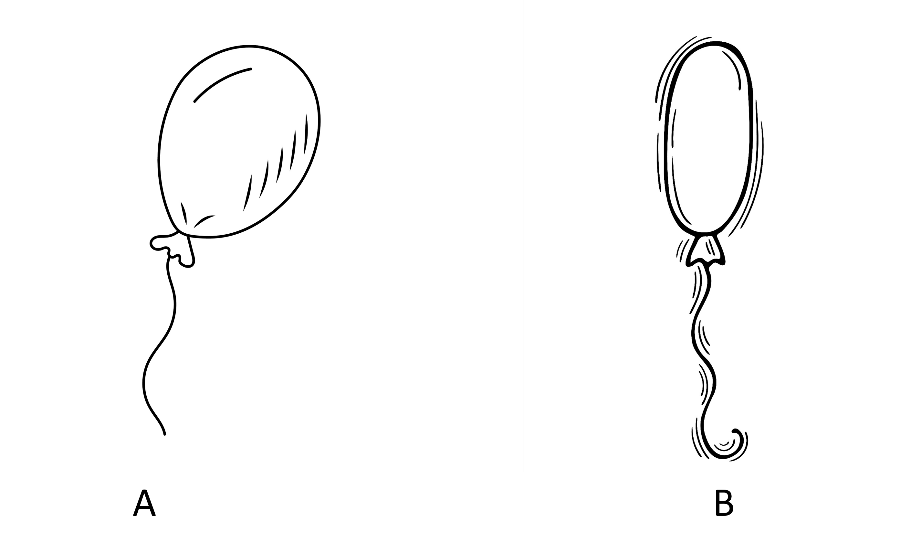
10. Two balloons are placed side by side. Balloon A is inflated fully, while Balloon B is only half-inflated.
Which balloon has more air pressure inside? (If equal, mark C)

A. a
B. a
C. c
Answer:
The correct answer is A.
The question asks us to compare the air pressure inside two balloons: fully inflated (Balloon A) and half-inflated (Balloon B).
Air pressure in a balloon is generally determined by the amount of air it contains and the volume it occupies.
A fully inflated balloon is generally stretched more tightly than a half-inflated balloon, and therefore, the air molecules inside are compressed into a smaller volume than they would be in a half-inflated balloon. This compression results in higher air pressure.
So, in this scenario, Balloon A, which is fully inflated, would generally have more air pressure inside it than Balloon B, which is only half-inflated.
Looking for the CAST Mechanical Preparation
The Edison Electric Institute CAST is your ticket to a career in the electrical and energy sectors.
Our CAST PrepPack covers everything you need to know – from technical topics like thermodynamics to cognitive skills such as Math and Spatial Reasoning.
Join now for only $79 and boost your chances of success with expert-led practice.
Worth every penny!
"I took the test for the first time 7 months ago and failed. This time got the test prep and passed! Thought it was way easier after taking the test prep".
Steve N. On CAST Test Prep
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (More reviews)
Thermodynamics questions can also be found in our IBEW PrepPack, EEI TECH PrepPack, EEI MASS PrepPack, and NJATC PrepPack.
Let’s continue to Simple Machines – concerning mainly Pulleys and Cogwheels.
Simple Machines
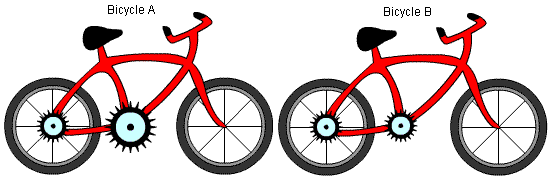
11. Two bicycles are shown in the diagram below. On which bicycle will it be easier to pedal while ascending a hill?
A. Bicycle A
B. Bicycle B
C. Both
D. Impossible to answer
Answer:
The correct answer is 2.
In order to answer questions of this type, we need to be familiar with the concept of gear ratio, also known as transmission ratio.
Gear ratio is defined as the ratio between the wheel upon which the force is applied and the wheel to which the force is transmitted.
Ninput = the number of teeth in the driver gear (driver cogwheel)
Noutput = the number of teeth in the driven gear (driven cogwheel)
-> Gear ratio = 
We can see from the diagram that the driver cogwheel in bicycle A is bigger than in bicycle B, whilst the driven cogwheel remains the same.
In accordance with the formula, we can see that the transmission ratio of bicycle B is greater than the transmission ratio of bicycle A (the transmission ratio is inversely proportional to the size of the driver cogwheel). Thus, the correct answer is bicycle B.
In this type of question, it might be easier for you to think of the transmission ratio in a more abstract way. For example, "When I turn the driver cogwheel once, how many times will the driven cogwheel turn?";
in this case, when the driver cogwheel in bicycle A turns once, it will cause more turns of the driven cogwheel in comparison to bicycle B.
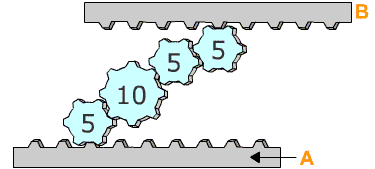
How does raft B move if raft A moves left at constant velocity?
(The digit in the circle represents the number of cogs of the gear)
A. Left with a greater velocity
B. Right with the same velocity
C. Left with the same velocity
D. Right with a greater velocity
E. Right with a lower velocity
Answer:
The correct answer is (C) – Left with the same velocity.
When raft A moves left, it applies a force on the 5-toothed gear attached to it, causing it to rotate clockwise.
Since the system given above consists of an even number of 4 meshed gears, the 5-toothed gear attached to raft B will rotate anti-clockwise.
This movement will apply a force on raft B, causing it to move left as well. This eliminates answers B, D, and E.
When two gears of equal number of teeth are combined, they rotate at the same velocity. Since the first and last gears of this meshed gear system have the same number of teeth, they will move at the same velocity.
Therefore, Left with the same velocity is the correct answer.

Tip: In a pulley system, the more pulleys there are, the easier it is to lift a weight, but you'll have to pull more rope.
When solving simple machine questions, identify the number of pulleys, the direction of force, and any other relevant factors.
Confirm the direction in which each wheel or pulley will turn based on the initial force or motion.
One final thing – if you have time, quickly verify if your answer makes sense. For example, in a multiple-pulley system, the force required to lift a weight should be less than the weight itself due to the mechanical advantage.
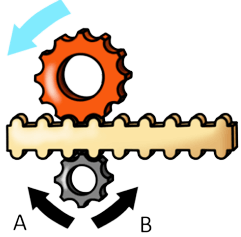
13. In which direction does the grey wheel turn? (If neither, mark C.)
A. a
B. b
C. c
Answer:
The correct answer is A.
When contact is made between the rack (toothed belt) and the cogwheels, a conversion occurs from linear to angular velocity. The location of the point of contact is critical.
The point of contact between the red cogwheel and the rack is in the lower part of the red cogwheel. The counterclockwise angular velocity induces a linear velocity to the right.
The point of contact between the grey cogwheel and the rack is in the grey cogwheel's upper part. The linear velocity to the right (determined by the rack) induces an angular velocity in a clockwise direction.
The process can be exemplified by the blue arrows, which show where each part of the wheel is moving under the rotation conditions:
Simple Machine questions – which mostly include either wheels and pulleys or cogwheels, usually require prediction about outcomes of specific actions – either movement of objects, direction of rotation, or other options.
Simple Machines questions can be found in our Bennett PrepPack, Plumber Apprenticeship PrepPack, Ergometric FireTEAM PrepPack, and DAT ( Differential Aptitude Tests) PrepPack.
Let’s look at another Mechanical Aptitude question type – Force and Movement. This is a common topic in mechanical tests and is found in most assessments, including Ramsay Mechanical and Maintenance exams. Let’s proceed.
Force and Moment Sample Question
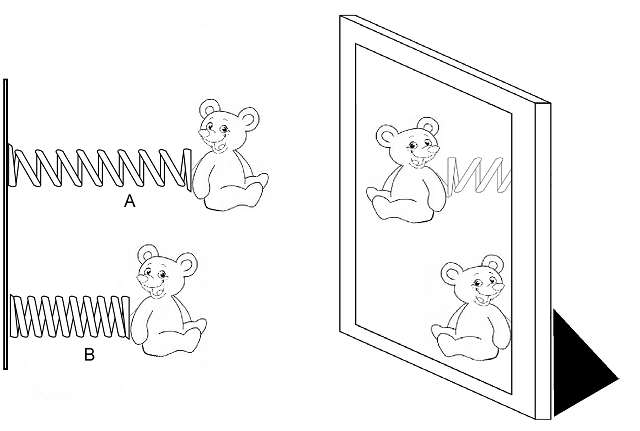
Two teddy bears are connected to 2 identical springs that are compressed to different extents.
Which teddy bear will travel closer to its reflection in the mirror when the springs are released?
*Assume both springs do not reach the mirror, even when fully extended.
A. a
B. b
C. c
Answer:
The correct answer is B.
We are asked in this question to determine which bear will get closer to the mirror.
When a spring is compressed, energy is stored in the spring. The more one compresses the spring, the larger the amount of energy that gets stored in the spring. When the spring is released, so is the energy; this energy then causes the spring to expand.
The larger the amount of energy, the greater the force expanding the spring. This, in turn, causes the spring to expand farther. Therefore, the more one compresses a spring, the farther the spring will expand when released.
Since Spring B is more compressed than Spring A, it will reach farther when released. Therefore, choice B is the correct answer.
15. A dancer is doing an act on a seesaw. As you can see, the seesaw is tilted. Assuming he can remain stable, to what position should he switch in order to balance the seesaw?

A. a
B. b
C. c
Answer:
A seesaw is an example of a first-class lever, where the fulcrum is in the middle and both forces (effort and load) are applied onto both sides of it.
In order for the seesaw to be balanced, the torque applied by the dancer must increase. Since the weight of the dancer remains the same, the only way to increase the input torque is by increasing the distance from the fulcrum.
In position B, even though the location of the dancer’s hands is the same as in A, the body’s center of mass is more distant from the fulcrum, and thus the input torque would be greater.
This will make it more likely for the seesaw to be balanced.
The correct answer is B.
Force and Moment questions can also be found in our Free Ramsay Mechanical Practice, Bennett PrepPack, Wiesen PrepPack, and Delta BMAR PrepPack.
List of Mechanical PrepPacks
You can find here the full list of the most common Mechanical Tests PrepPacks, which include different questions aimed to provide precise practice and prepare you for your upcoming test:
Mechanical Aptitude Test FAQs
Our Mechanical Aptitude Test covers a variety of topics designed to assess your understanding of mechanical principles and problem-solving skills.
In our pack, you’ll find practice questions that mirror the real test, including:
- Fundamental Mechanics: Challenges on levers, gears, pulleys, and simple machines.
- Visual-Spatial Reasoning: Questions that test your ability to interpret diagrams and understand spatial relationships.
- Practical Problem-Solving: Real-world scenarios where you apply mechanical concepts to troubleshoot and predict outcomes.
Using our pack, you can practice with these question types, ensuring you’re fully prepared and confident on test day.
There isn’t one magic trick—but there is a proven approach. Our pack offers a systematic way to succeed by helping you:
- Master the Fundamentals: Our study guides break down core mechanical concepts so you understand the "why" behind every question.
- Practice Strategically: With realistic practice tests and detailed answer explanations, you learn to spot patterns and common pitfalls.
- Build Confidence: Regular practice with our materials builds your test-taking confidence, making the real test feel like a breeze.
By using our pack, you’re adopting the same strategies that have helped thousands of job seekers ace their tests.
While there’s no shortcut to instant success, our pack equips you with the tools to approach each question with a clear strategy:
- Understand and Simplify: Our resources teach you how to break down complex problems into manageable parts.
- Use Process of Elimination: Learn techniques to quickly eliminate wrong answers, boosting your accuracy.
- Practice Under Real Conditions: Our timed practice tests simulate the actual exam environment, helping you refine your time management skills.
The step-by-step strategies in our pack have been developed and refined by experts to give you the competitive edge needed to excel.
Many candidates initially find aptitude tests challenging, but with the right preparation, they become highly manageable.
Our pack is designed to make your preparation as smooth as possible by offering:
- Targeted Practice: Focus on the areas that need improvement with customized practice tests.
- Detailed Feedback: Instant, actionable insights that help you learn and improve with every practice session.
- Proven Strategies: Techniques that thousands of successful job seekers have used to overcome challenges and excel in their tests.
With our comprehensive pack, you’ll see that what once seemed difficult becomes just another opportunity to demonstrate your true potential.
The test not only measures your current aptitude but also highlights key areas that you can focus on to boost your performance in job interviews.
With personalized insights and recommendations, you’ll be better equipped to answer technical questions confidently and demonstrate your problem-solving abilities to potential employers.
After completing the free test, you’ll have the option to access our in-depth study guides, practice questions, and video tutorials—resources that have already helped over 1,500 job seekers elevate their skills and secure better job opportunities.
These materials are designed to offer you a comprehensive preparation experience, whether you’re aiming for an interview or seeking career advancement.
Here are the key differences between different mechanical tests:
- Mechanical knowledge covers a broader range of understanding, including how things work, how to maintain and repair them.
- Mechanical comprehension tests reasoning and spatial understanding of mechanical principles.
- Basic mechanical aptitude focuses on assessing fundamental skills and understanding of simple mechanical tasks and tools.




