The Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory (HBRI) assessment is a challenging test that measures problem-solving abilities with 24 questions of different types:
- Numerical Reasoning
- Logic & Verbal Reasoning
- Abstract Reasoning
Passing the Hogan HBRI test requires using the right technique to quickly solve questions within the 30-minute time limit, which can get stressful when so much is on the line.
To ensure the best possible result, accurate practice is crucial.
Our online HBRI preparation pack provides timed Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory practice tests with detailed answers, which will sharpen your skills and get you ready to solve any question. To get a glimpse of it, skip to HBRI sample questions and answers.
See the following page for our All-Inclusive Hogan Preparation.
- 5 Full Hogan HBRI simulations
- Over 40 practice tests:
numerical, verbal & abstract reasoning - Math & verbal guides and tutorials
- Supplementary guides & practice drills
What Is the Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory (HBRI)?
There are several different Hogan Assessments, each designed to measure various skills, and you should practice for all of them. One of the tests is the Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory (HBRI), which focuses on evaluating your cognitive skills. The HBRI assessment consists of 24 questions that require you to draw conclusions from complex data sets, helping employers gauge your reasoning style, data analysis skills, problem-solving abilities, and decision-making effectiveness.
- Is the HBRI test timed?
Yes, the HBRI test requires solving 24 questions within 30 minutes. There had also been an earlier unlimited version of the exam.
Keep reading for sample questions and explanations on the HBRI test
What Kind of Questions Can You Expect on the HBRI Test?
The HBRI test has 24 multiple-choice questions of three types:
Numerical Reasoning Questions
Numerical questions include word problems and various math questions. These require being able to calculate percentages, dimensions, etc. based on data presented in tables, charts, graphs, and diagrams.
For example, try solving the following question:
Observe the following table:
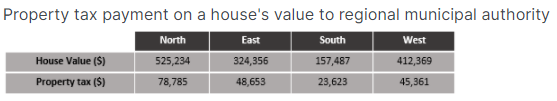
Which regional municipal authority is not paid the correct property tax, compared to the others?
Abstract Reasoning Questions
Abstract reasoning questions require analyzing and manipulating 2-D and 3-D figures.
For example, try solving the following question:
Which of these sitting arrangement charts is identical to the original, but rotated clockwise?
Original:
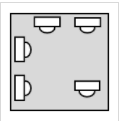
Answers:
Verbal Reasoning & Logic Questions
Verbal reasoning and logic questions require solving word analogies and logic riddles.
For example, try solving the following question:
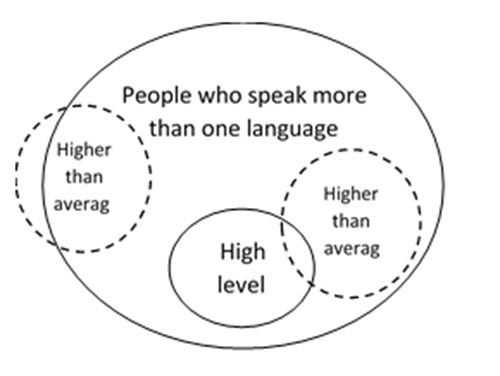
- All high-level managers speak more than one language.
- Some people who speak more than one language have a higher than average IQ.
Which of the following must true?
You can solve more sample questions from HBRI or other Hogan tests, by taking our sample Hogan test.
Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory Sample Questions
Take a look at some other forms of Hogan HBRI sample questions and answers, taken from our full Hogan HBRI practice course:
Business Reasoning #1
*Source - JobTestPrep Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory practice test.
Business Reasoning #2
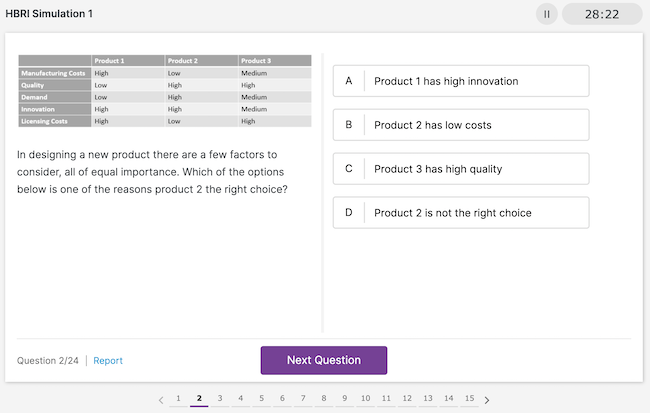
*Source - JobTestPrep Hogan HBRI practice test.
Looking for more HBRI practice questions & answers? Access our full online HBRI practice and get timed Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory practice tests, solving tips, guides, and tutorials.
What Does the HBRI Measure?
Hogan is a cognitive ability test, like the Criteria CCAT. The HBRI score report provided by Hogan to the employer goes into great detail regarding your cognitive style, based on two components of critical reasoning:
- Qualitative Reasoning – your ability to solve problems based on visual data, logic and verbal information.
- Quantitative Reasoning- your ability to solve problems based on mathematical and spatial information.
The combination of these two reasoning styles is used to explain your general cognitive style. For example, if you score high on qualitative reasoning and low on quantitative reasoning, you would likely identify important problems, but minimize the implications of practical steps needed to solve them.
- Expedient Thinker – typically analyzes problems opportunistically, chooses answers that are quick and easy, and makes intuitive rather than reflective choices, leading to poor-quality solutions.
- Contextual Thinker – typically identifies important problems but ignores the obstacles to their solution and minimizes the importance of the detailed steps needed to solve them.
- Analytic Thinker - typically focuses on a problem and the obstacles to its solution, without putting the problem in a larger context and evaluating the need for its immediate resolution.
- Critical Thinker - This is the most effective type of reasoning style, that combines high qualitative and quantitative reasoning. It means you’ll effectively identify problems, evaluate the short- and long-term benefits of their solution, and implement the most effective ones.
Hogan HBRI Sample Report
The Hogan business reasoning inventory assessment results are given to employers as three types of scores: qualitative reasoning score, quantitative reasoning score, and an overall business reasoning score.
The overall business reasoning score indicates your ability to solve complex problems, relative to other candidates. This is how it would look like:
The higher the HBRI assessment score on your Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory, the higher your chances are to stand out as a successful problem-solver and outshine your competition.
How to Prepare for the HBRI Assessment?
Getting familiar with all the HBRI assessment questions, taking timed HBRI practice tests, and getting full answers and feedback can greatly improve your solving speed and accuracy in this complex test.
Our team of experts has created a unique online preparation for the Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory, that hundreds of our customers found extremely helpful. Most importantly, it allowed them to complete this exam confidently, as they were familiar with and skilled in solving the type of questions they encountered on the actual Hogan HBRI test.
Note: If you’ve been asked to take both Hogan’s HBRI and HPI assessments, we recommend our bundle HBRI+HPI practice pack.